|
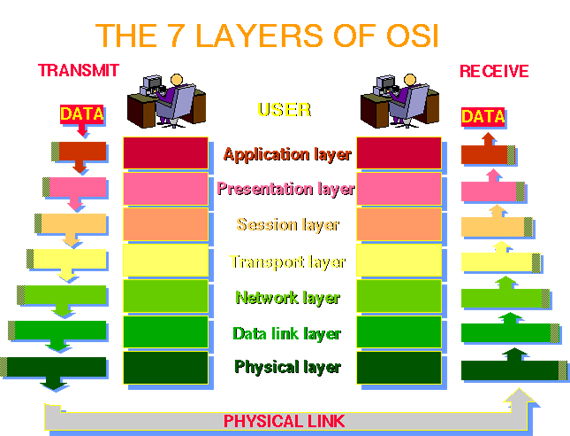
Layer
|
Function |
Protocols |
Network Components |
|
Application
User Interface
|
- used for applications specifically written to
run over the network
- allows access to network services that
support applications;
- directly represents the services that
directly support user applications
- handles network access, flow control and
error recovery
- Example apps are file transfer,e-mail,
NetBIOS-based applications
|
DNS; FTP; TFTP; BOOTP;
SNMP;RLOGIN; SMTP; MIME; NFS; FINGER; TELNET; NCP; APPC; AFP;
SMB |
Gateway |
|
Presentation
Translation
|
- Translates from application to network format
and vice-versa
- all different formats from all sources are
made into a common uniform format that the rest of the
OSI model can understand
- responsible for protocol conversion,
character conversion,data encryption / decryption,
expanding graphics commands, data compression
- sets standards for different systems to
provide seamless communication from multiple protocol
stacks
- not always implemented in a network protocol
|
|
Gateway
Redirector |
|
Session
"syncs and sessions" |
- establishes, maintains and ends sessions
across the network
- responsible for name recognition
(identification) so only the designated parties can
participate in the session
- provides synchronization services by planning
check points in the data stream => if session fails,
only data after the most recent checkpoint need be
transmitted
- manages who can transmit data at a certain
time and for how long
- Examples are interactive login and file
transfer connections, the session would connect and
re-connect if there was an interruption; recognize names
in sessions and register names in history
|
NetBIOS
Names Pipes
Mail Slots
RPC |
Gateway |
|
Transport
packets; flow
control & error-handling |
- additional connection below the session layer
- manages the flow control of data between
parties across the network
- divides streams of data into chunks or
packets; the transport layer of the receiving computer
reassembles the message from packets
- "train" is a good analogy => the data is
divided into identical units
- provides error-checking to guarantee
error-free data delivery, with on losses or duplications
- provides acknowledgment of successful
transmissions; requests retransmission if some packets
donít arrive error-free
- provides flow control and error-handling
|
TCP, ARP, RARP;
SPX
NWLink
NetBIOS / NetBEUI
ATP |
Gateway
Advanced Cable Tester
Brouter |
|
Network
addressing; routing
|
- translates logical network address and names
to their physical address (e.g. computername ==> MAC
address)
- responsible for
- addressing
- determining routes for sending
- managing network problems such as packet
switching, data congestion and routing
- if router canít send data frame as large as
the source computer sends, the network layer compensates
by breaking the data into smaller units. At the
receiving end, the network layer reassembles the data
- think of this layer stamping the addresses on
each train car
|
IP; ARP;
RARP, ICMP; RIP; OSFP;
IGMP;
IPX
NWLink
NetBEUI
OSI
DDP
DECnet |
Brouter
Router
Frame Relay Device
ATM Switch
Advanced Cable Tester |
|
Data Link
data frames to bits
|
- turns packets into raw bits 100101 and at the
receiving end turns bits into packets.
- handles data frames between the Network and
Physical layers
- the receiving end packages raw data from the
Physical layer into data frames for delivery to the
Network layer
- responsible for error-free transfer of frames
to other computer via the Physical Layer
- this layer defines the methods used to
transmit and receive data on the network. It consists of
the wiring, the devices use to connect the NIC to the
wiring, the signaling involved to transmit / receive
data and the ability to detect signaling errors on the
network media
|
Logical Link Control
- error correction and flow control
- manages link control and defines SAPs
802.1 OSI Model
802.2 Logical Link Control |
Bridge
Switch
ISDN Router
Intelligent Hub
NIC
Advanced Cable Tester |
Media Access Control
- communicates with the adapter card
- controls the type of media being used:
802.3 CSMA/CD (Ethernet)
802.4 Token Bus (ARCnet)
802.5 Token Ring
802.12 Demand Priority |
|
Physical
hardware; raw bit
stream |
- transmits raw bit stream over
physical cable
- defines cables, cards, and physical
aspects
- defines NIC attachments to hardware,
how cable is attached to NIC
- defines techniques to transfer bit
stream to cable
|
IEEE 802
IEEE 802.2
ISO 2110
ISDN |
Repeater
Multiplexer
Hubs
TDR
Oscilloscope
Amplifier |